NASA Earth Observatory.
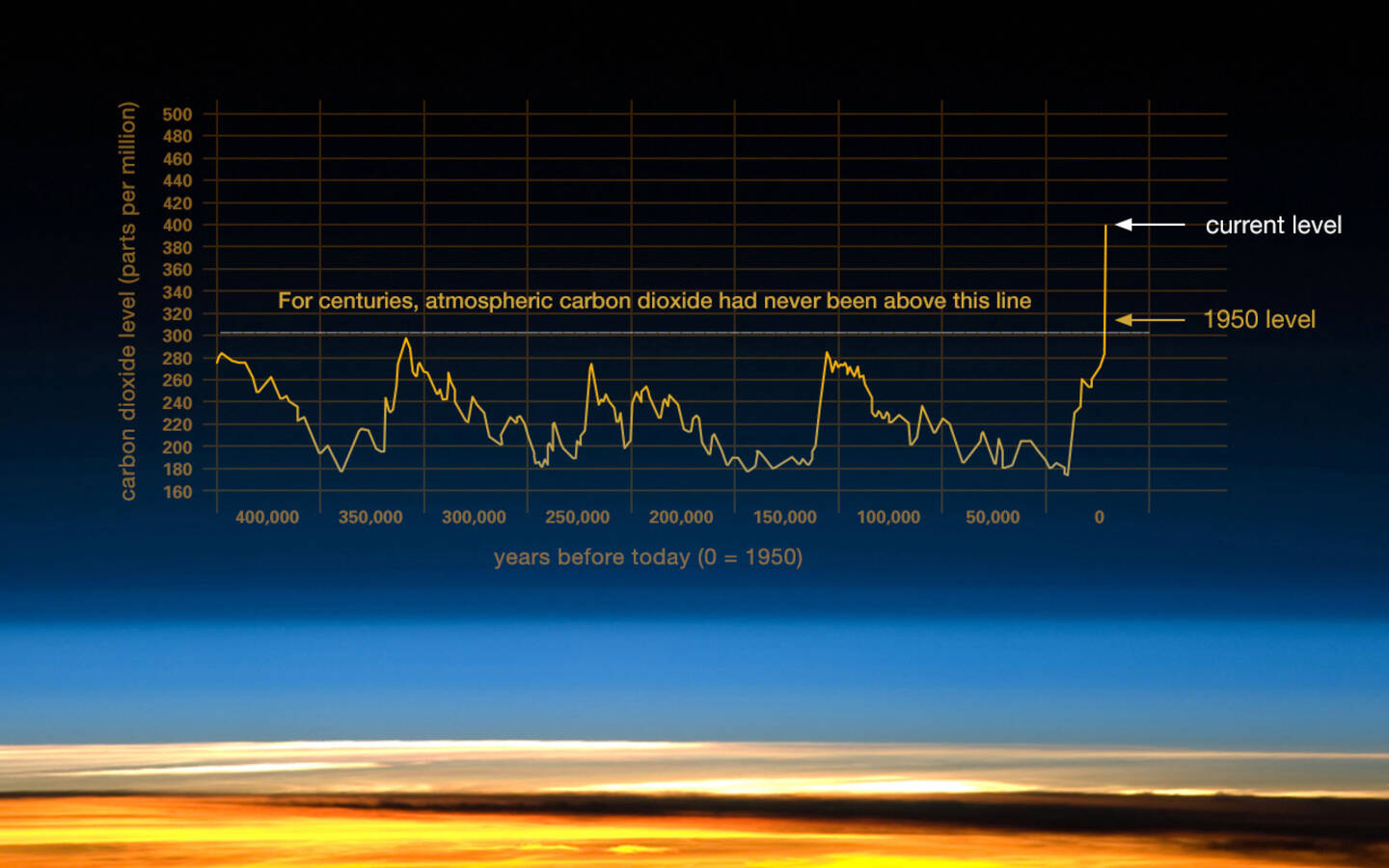
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is an important heat-trapping (greenhouse) gas, which is released through human activities such as deforestation and burning fossil fuels as well as natural processes such as human respiration and volcanic eruptions. The graph shows carbon dioxide levels during the last three glacial cycles, as reconstructed from ice cores, and the extraordinary rise of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere beginning in 1950. The concentration of carbon dioxide in the lower atmosphere is listed in parts per million (ppm). All recent measurements of carbon dioxide are at the observatories on Mauna Kea on the island of Hawaii, a remote location that well illustrates the growing worldwide increase of the gas. 2016.
